Periodontal Disease
The early signs of Periodontal Disease are redness and swelling of the gingivae
which also bleed easily. However, it should better be confirmed by the dentist's
diagnosis.
Mild Periodontal Disease
Symptoms
• Gingival margin is red and swollen
• Gingivae (gum) bleed easily upon toothbrushing
• Calculus may be accumulated
• The teeth or gingivae may be painful
• Bad breath

Management
• Use oral care products such as toothbrush,
dental floss, etc. to remove the dental plaque everyday
in the morning and before bed at night.
• If calculus is present, have it removed by scaling by the dentist in order
to facilitate your daily removal of dental plaque.
Then, the area with mild Periodontal Disease will heal by itself.
Moderate Periodontal Disease
Symptoms
• Gingival margin shows marked redness and swelling
• Gingivae always bleeds upon toothbrushing
• Gingival margin recedes, leading to the exposure of the root of the tooth
and the tooth looks longer
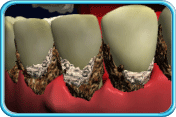
• Periodontal pocket is formed (The inflammation of periodontal
tissues leads to the destruction of periodontal membrane.
The periodontal tissues and the root of the tooth become detached and a periodontal
pocket is formed in between.)
• Calculus is accumulated
• Bad breath
• The teeth or gingivae may be painful
Management
• Go and see a dentist immediately for scaling
to remove the calculus and the dental plaque in the
periodontal pocket. After the removal of calculus, it will be easier to thoroughly
remove the dental plaque.
• Use oral care products such as toothbrush,
dental floss, etc., to remove the dental plaque everyday in the morning and before
bed at night in order to prevent Periodontal Disease from progressing or recurring.
• After treated by a dentist, you must maintain good oral care habits and visit
the dentist regularly for oral check-up.
Severe Periodontal Disease
Symptoms
• Gingival margin shows marked redness and swelling
• Gingivae always bleed during tooth brushing
• Periodontal tissues recede markedly and the tooth looks longer and longer
• Periodontal pocket is formed, pus exudes from the gingival margins and periodontal
abscess may be formed
• Calculus is accumulated
• Bad breath
• The teeth or gingivae may be painful
• The affected tooth becomes loose and drifts away from its original position
• The affected tooth may even fall out

FAIL (the browser should render some flash content, not this).
Management
• See a dentist immediately for:
• Scaling to remove the calculus
• Root planing or periodontal
surgery to remove the dental plaque and calculus on the roots of the teeth
and in the periodontal pockets.
• Receive antibiotic therapy as needed
• Use oral care products such as toothbrush,
dental floss, etc. to thoroughly remove dental plaque everyday in the morning and
before bed at night so as to control the progression of the disease.
• After treated by a dentist, you must maintain good oral care habits and visit
the dentist regularly for oral check-up.